
Ways To Treat Scars
The larger and more painful the inflammation, the less likely it is to disappear without a trace. Therefore, to reduce the likelihood of dark spots, you need to stop the inflammatory process, preventing it from developing and causing serious damage to the skin. For this, products for problem skin are useful, providing an antiseptic, soothing and/or drying effect.
If it is not possible to prevent the appearance of post-acne, work begins on the removal of excess pigment. The simplest (but not the most effective) method is mechanical exfoliation. Helping the skin to renew itself in this way, we also remove particles containing excess pigment, gradually returning to a smooth, even tone. But taking into account the fact that we are talking about skin that is recovering from an injury, this process should be as gentle as possible.
The action of such peeling gels is just aimed at gentle, delicate exfoliation. They do not contain coarse, sharp abrasive particles that injure the skin: the effect occurs due to acrylates and cellulose fibres, which are collected into small lumps upon contact with sebum. These “pellets” provide mechanical removal of keratinized particles – very soft and not traumatic.
The use of peelings in the fight against post-acne is recommended for owners of sensitive skin and those who, for whatever reason, cannot use chemical exfoliants. Acting only in the uppermost layer of the skin and providing a momentary effect, they will be effective in combating light, shallow spots.
Several ingredients can gradually reduce pigmentation with regular use, either by stimulating the skin’s natural renewal process or by blocking melanin production.
Such components will be most effective in the composition of products that require a long exposure time: creams, essences, masks, etc. – skin cleansers containing them can be a good addition to the main care system, but they are unlikely to cope with the problem on their own.
Some Recommended Ingredients:
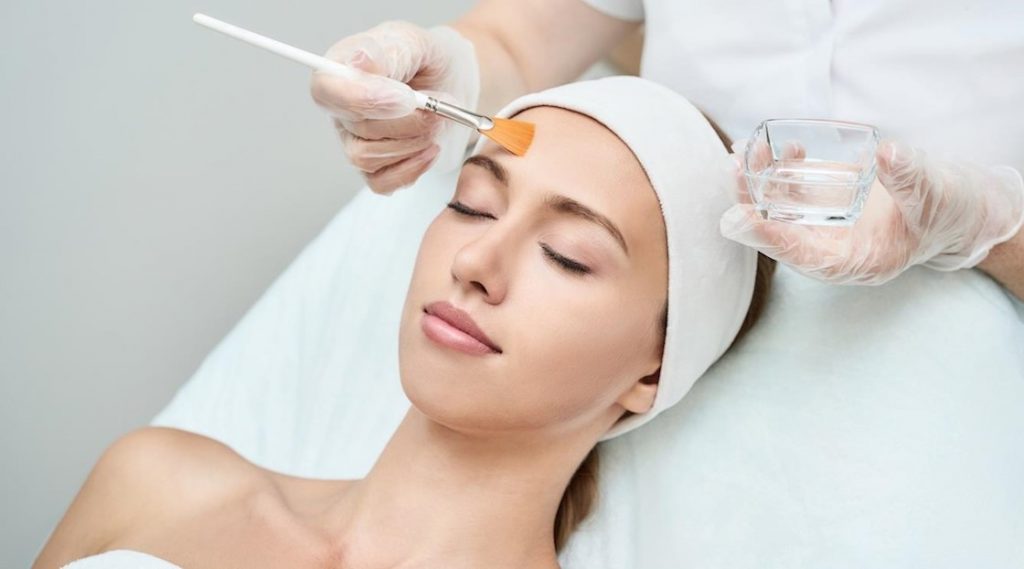
The removal of dead cells can occur not only with the help of mechanical friction – this function is performed by many components in the compositions of serums, creams, lotions, masks and other cosmetic products that require regular use and provide a gradual effect.
Glycolic acid
One of the most popular components of “renewal” care: is glycolic acid molecules are smaller than other AHAs, which means they can penetrate deeper into the skin. It stimulates the processes of skin renewal, exfoliates dead particles, restores a healthy glow and helps even out tone.
Lactic acid
The action of lactic acid (which also belongs to AHA acids) is much more gentle than that of glycolic. It is the main component of the natural moisturising factor (a complex of molecules in the stratum corneum that are responsible for retaining moisture in it), therefore it is suitable for the care of dry skin.
Enzymes
In their effect, enzymes (protein molecules that can break down protein bonds between dead cells) are similar to acids but have a larger molecule size, which means they provide an even more superficial (but also softer) effect.
Topical (topical) retinoids
Retinoids (the most popular of which is vitamin A/retinol) accelerate the rate of skin cell renewal but compared to AHA acids and enzymes, they act deeper: not only in the stratum corneum but also at deeper levels of the epidermis. Due to this, they are not only effective in the fight against post-acne but also help to solve the “root” problem, normalising the production and composition of sebum and preventing the appearance of comedones.
Important: the use of retinoids is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In cosmetics, vitamin C is often found in the form of ascorbic acid – it begins to act immediately after application and is therefore considered the most effective. For sensitive skin, products with ascorbic acid derivatives are suitable – their effect is not so pronounced, but they practically do not irritate. In any form, this ingredient interferes with the production of melanin and transforms existing pigment molecules, making them colourless.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, is a real “superhero” ingredient. It is credited with the ability to smooth the surface, restore the protective barrier of the skin, prevent the appearance of imperfections – and, of course, fight pigmentation disorders. Moreover, it works even in very small concentrations.
So, at your disposal is a whole arsenal of tools for returning a healthy, even tone. However, when choosing a comprehensive care system aimed at combating post-acne, one should also not forget about the basic needs of the skin: moisturising, maintaining tone and protection from external influences.
First, determine its type ( our detailed article on skin types will help you with this ) and basic needs, assess the severity of post-acne and exclude the possibility of allergic reactions, and then – on your own or with the help of a dermatologist – choose the helpers that suit you, starting from these criteria.




